Determination of temperature and enthalpy of melting-crystallisation
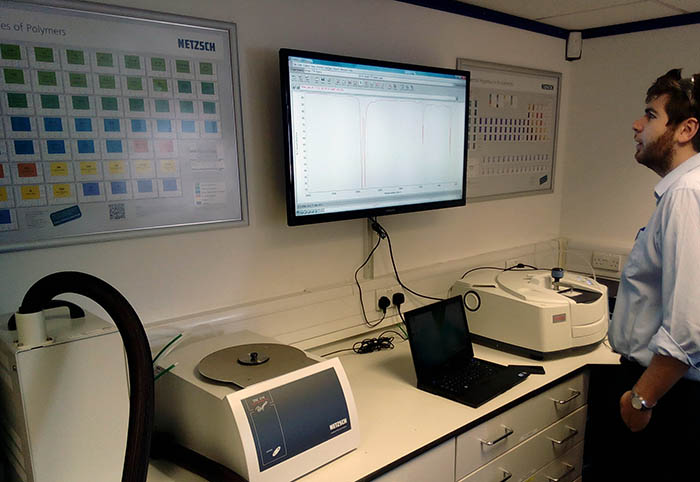
Semi-crystalline plastics, when heated, pass from the crystalline (solid) stage to the molten (soft) phase. Due to their different molecular structures, plastics melt at different temperatures. The most precise method to determine the temperature and enthalpy of melting (the melting properties) of the plastics is by differential scanning calorimetry (ISO 11357-3, ASTM D3418).
A small piece of plastic (approximately 10 mg) is heated and cooled at a controlled rate under nitrogen. During the heating and the cooling cycles, the following parameters are obtained:
- melting of semi-crystalline plastics: transition stage between a fully crystalline or partially crystalline solid state and an amorphous liquid of variable viscosity
- crystallisation: transition stage between an amorphous liquid state and a fully crystalline or partially crystalline solid state
- enthalpy of fusion: heat required to melt material at a constant pressure
- enthalpy of crystallisation: heat released by the crystallisation of a material at a constant pressure