What is flash point testing?
With any conscious business, flash point testing is critical to ensuring safety. Simply put, the flash point of a material is the lowest temperature at which its vapours can ignite from an ignition source.
Determining the flash point becomes necessary to: assess the flammability of liquids and semi-solids and to classify the materials based on their flammability.
Knowing and understanding the flash point of the material helps in their safe storage, transportation, and usage. Materials with lower flash points (their vapours can ignite at lower temperatures) are more hazardous and will require special storage and handling compared to materials with higher flash points.
The Closed Cup Method
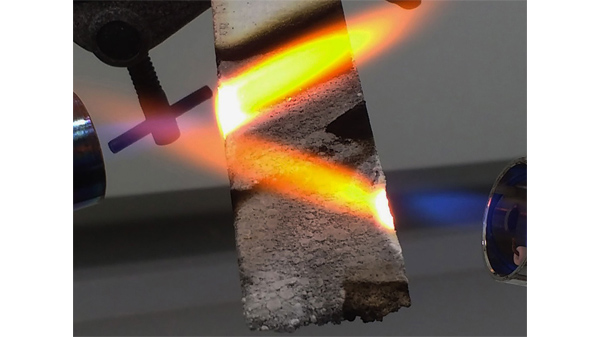
Impact Solutions perform flash point testing using our Rapid Tester Close Cup method. The close-up method involves heating the vessel and sample together and introducing a flame source to ignite the vapours generated. This creates a visible flash and the temperature at which this happens is recorded as the flash point of that material.
The temperature range that can be tested using a gas ignition source is 300C to 3000C.
The advantages of this method are:
- Simulates real life hazards and more accurate than open cup method.
- Preferred industry standard.
- Small sample size (2 ml – 4) ml makes it most suitable for R&D and where samples are scarce.
Examples of typical materials tested include oils, petrochemicals, paints, solvents, adhesives, inks, cleaning products, asphalt, pesticides, and chemicals.