What is the Bell Telephone Test
Where did the name come from?
The Bell Telephone Test earned its name due to its origin and initial use in the Bell Laboratories. Bell Laboratories, historically associated with the American telecommunications company Bell Telephone System (later known as AT&T), was renowned for its extensive research and development efforts in various fields, including materials science and engineering.
What does the bell telephone test involve?

test oil bath
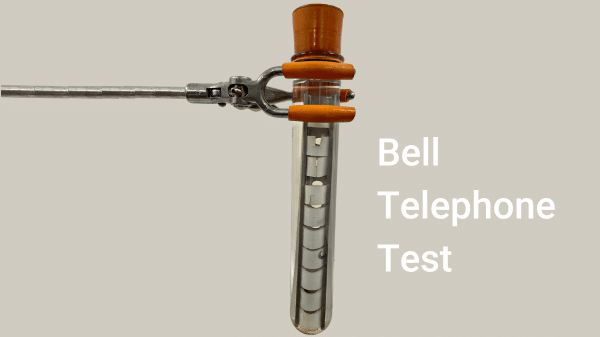
The test (ASTM D1693) involves a short notched plate of material, which is bent and held in a holder and immersed in the test fluid. Typically, the test fluid is a detergent solution (very specifically Igepal CO630) to accelerate cracking and the test takes place at an elevated temperature, e.g. 50°C, by immersing the test assembly in a heated bath. However depending on the application, the plastic will be used for, the temperature can be varied, and the solution used varied to simulate the expected conditions that the plastic will have to endure.

stress crack example
The stress crack example shows the typical mode of failure in this test, which must be observed and recorded as a function of time. The material is regarded as having failed when 50% of the test specimens show some incipient failure. There are different specifications of test geometry according to the classification of the material, i.e. LDPE or MDPE/HDPE. The method is simple and gives good indications of performance.
Other methods of ESCR?
Exploring other methods of ESCR, Impact Solutions holds UKAS accreditation for both the Bell Telephone Test and ISO 16770, known as the Full Notch Creep Test (FNCT). The FNCT offers a distinct approach to measuring stress crack resistance in polyethylene. Unlike the Bell Telephone Test, the FNCT utilizes a full-notch specimen subjected to varying loads over time to evaluate stress crack resistance. The key disparity between these tests lies in their methodologies, with the Bell Telephone Test employing a bent strip immersed in a specific solution at elevated temperatures, while the FNCT relies on a full-notch specimen under varied loads to assess stress crack resistance.