NMR of PMMA – tacticity and its determination through NMR
In polymers, tacticity is the ordered configuration, or lack thereof, of pendant groups branching off of the main backbone. Take polypropylene for example, where the methyl branch can repeatedly point out of the screen (isotactic), alternate between pointing out and pointing in (syndiotactic), or be completely random (atactic):
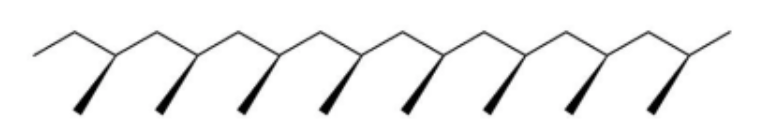
Isotactic
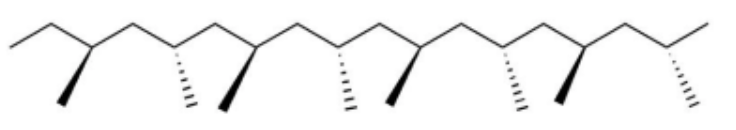
Syndiotactic
Atactic
The arrangement of these pendant groups has an effect upon the physical properties of the polymer. Atactic polypropylene, often called linear low density polypropylene, is an amorphous and soft material whereas isotactic polypropylene (high density polypropylene) is very strong, capable of being used in industrial water and gas piping.
Clearly, the tacticity of a polymer is essentially important with the application in mind. The effects upon the glass transition temperature with differing tacticity is particularly noticeable in poly(methyl methacrylate), PMMA. Pure isotactic PMMA gives a Tg of around 42 0C whilst pure syndiotactic tends to be closer to 124 0C.
Two grades of PMMA and a reference PMMA sample were provided to impact solutions with the customer querying what the difference between them was. We took the approach of analysing the tacticity through 1H NMR on our portable NMR on-site, obtained as part of a collaboration with ScotChem. The effects of this tacticity upon glass transition temperature was assessed on our DSC 214 Polyma.
Comparing the methylene –CH2– group in different tacticities tells us what to expect from the resultant NMR spectrum:
In isotactic PMMA, one methylene hydrogen is repeatedly exposed to the pendant group on the same side and therefore, the other methylene hydrogen is not in the same environment. This causes two peaks in the spectrum.
In syndiotactic PMMA, the methylene hydrogens both experience the pendant group alternatively, therefore they are in the same environment. This causes one peak.
Atactic PMMA will contain some syndiotactic regions and some isotactic regions, therefore all three peaks are observed.
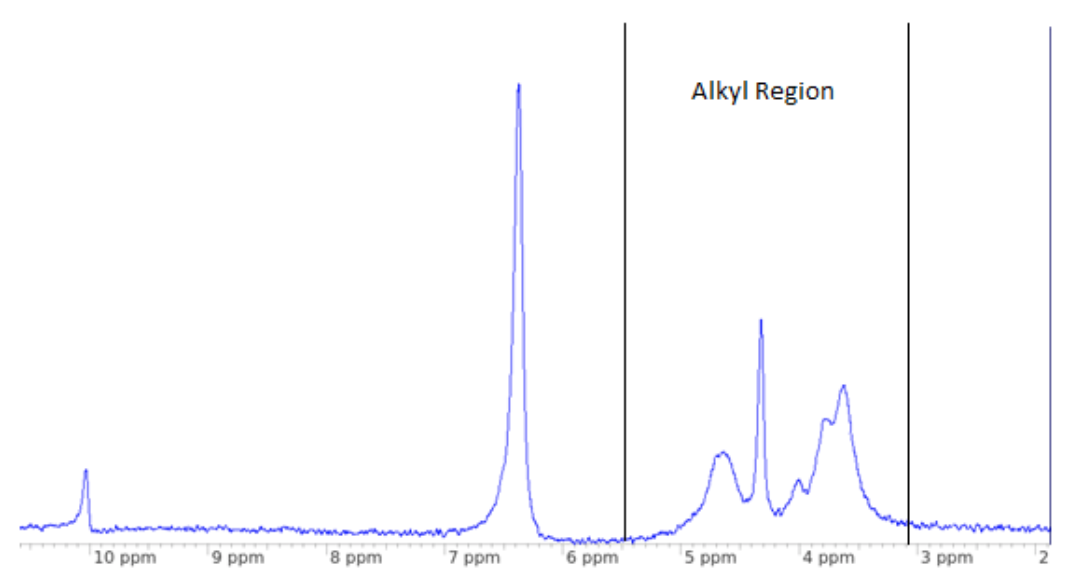
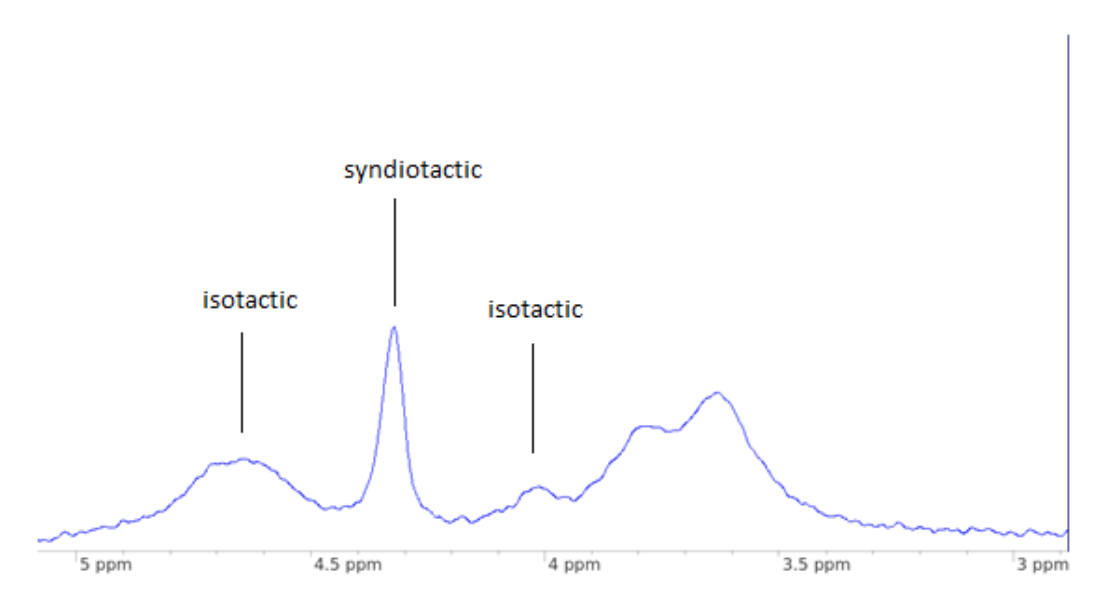
The reference sample produced an atactic spectrum which contains slightly more syndiotactic regions compared to isotactic. The Tg was determined to be 114 0C.
Comparing this with the second NMR of PMMA sample to be assessed:
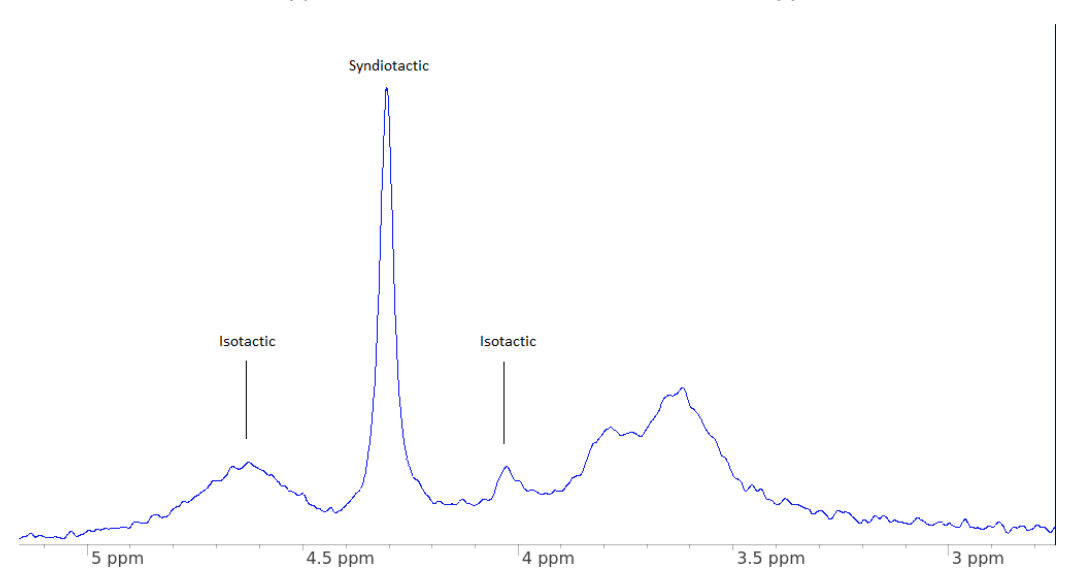
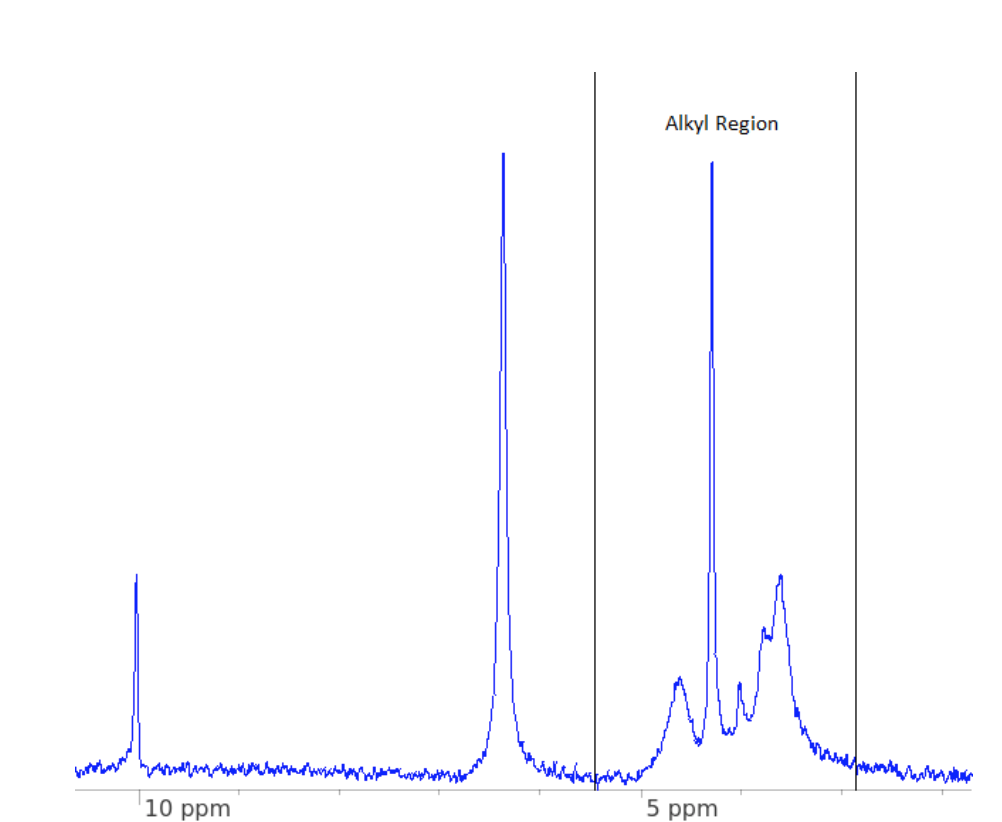
Despite again being atactic, it is clear that the proportion of syndiotactic regions has increased. This grade of PMMA is therefore predominantly syndiotactic, resulting in a higher Tg compared to the reference of 120 0C.
If you would like further information, please contact impact solutions today!
Be sure to keep up-to-date with our newest developments by following us on Facebook, LinkedIn and Twitter.